Desalination is a process that involves removing contaminants and excess salts from water in order to render it suitable for usage in a variety of contexts. This makes the water suitable for consumption as well. This method is able to purify brackish water, seawater, and wastewater, among other types of water. One of the primary drivers behind the expanding use of desalination plants for water is the ever-increasing global demand for water that is directly attributable to the ever-increasing human population.
The Reverse Osmosis Segment will dominate the Global Water Desalination Market
Reverse osmosis is the dominant segment in the market. This can be ascribed to the fact that it is simple to process, has a cheap installation cost, can treat multiple kinds of feed water, and requires a small amount of chemical treatment. The rising demand for desalination plants in areas of the world that are experiencing a shortage of fresh water is a major factor propelling the market's expansion.
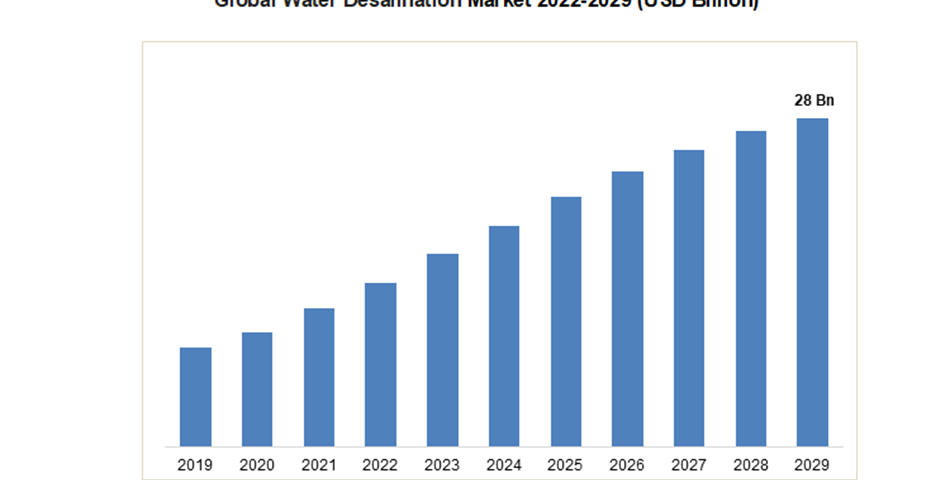
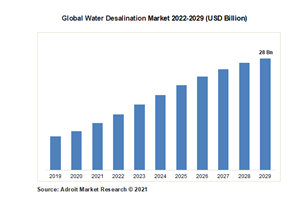
In 2020, the global market for water desalination equipment was estimated to be worth 13.12 billion US dollars. The market will expand 9.1% to 28.32 billion US dollars between 2022 and 2029.
Thermal and membrane processes are two of the many methods that can be utilized in the process of water purification. Due to the fact that just 3% of the earth's water supply is actually potable, water scarcity is one of the most pressing problems that need to be addressed in the years to come. At the moment, desalination only produces 1% of the drinking water that is used all over the world.
In addition to this, other factors that are predicted to drive the growth of the market include increasing urbanization, legislation for water conservation and use, and rising levels of consumer awareness regarding the need of drinking clean water. On the basis of the technology employed, the global market for water desalination may be broken down as follows: reverse osmosis (RO), multi-stage flash (MSF), and multi-effect distillation (MEF), as well as other categories. Because it does not require the addition of any other chemical to the incoming water and still produces water that is fit to be consumed despite the removal of dissolved salts, reverse osmosis has become the most popular method for purifying water. This is due to the fact that it does not involve the addition of any other chemical to the water.
Seawater is pumped into the plant during the desalination process and subjected to pretreatment. During this step, filtering is used to remove the suspended solids and other particles from the water. After this point, the water is either subjected to reverse osmosis or thermal distillation to get rid of the saltiness. The expansion of the global population at a rapid rate, combined with the depletion of freshwater sources, has led to an increase in the demand for water around the world, which has contributed to the expansion of the market. Compared to seawater, brackish groundwater has a significantly higher rate of recovery, which is the primary advantage of desalinating this type of water. Saltwater desalination produces roughly fifty percent freshwater, but brackish water desalination produces approximately ninety percent freshwater. In addition, the quantity of brine generated following the treatment of brackish water is lower in volume and more concentrated than the quantity of brine gained following seawater, making the method friendlier to the environment.
Recent Developments
- A French utility business and Saudi Arabia's National Water Co. (NWC) entered into a contract in January 2021 worth a total of USD 5.36 billion for a period of two years to reduce the quantity of water that is lost during the process of producing water for the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
- In October of 2020, Aguas Pacifico SpA presented IDE Technologies with an EPC contract for the Aconcagua Desalination Plant. The design and planning of a seawater reverse osmosis desalination plant, as well as its supply and construction, as well as its startup and commissioning, are all included in the scope of the project.
- It is anticipated that the facility will have a notional production capacity of 86,400 m3/day, which is equivalent to 1,000 liters per second. The project will be situated in the harbor of Quintero in the Valparaso Region of Chile. To meet the needs of municipal, agricultural, industrial, and mining customers in the area, the facility will be the first source of fresh water in the Aconcagua basin that is resistant to the effects of drought.