Make delicious purified drinking water under your sink with a reverse osmosis water filtration system.
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis removes contaminants from unfiltered water, or feed water, when pressure forces it through a semipermeable membrane. Water flows from the more concentrated side (more contaminants) of the RO membrane to the less concentrated side (fewer contaminants) to provide clean drinking water. The fresh water produced is called the permeate. The concentrated water left over is called the waste or brine.
A semipermeable membrane has small pores that block contaminants but allow water molecules to flow through. In osmosis, water becomes more concentrated as it passes through the membrane to obtain equilibrium on both sides. Reverse osmosis, however, blocks contaminants from entering the less concentrated side of the membrane. For example, when pressure is applied to a volume of saltwater during reverse osmosis, the salt is left behind and only clean water flows through.
To reduce contaminants from drinking water or improve the taste and smell of tap water, water filters in refrigerators and pitchers can do the job. But, to take water purification to the next level, consider a reverse osmosis water filtration system.
A reverse osmosis (RO) water system integrates with the plumbing under your kitchen sink to force water through a semipermeable membrane and a series of filters, removing sediment and contaminants, providing dozens of gallons of purified water each day.
How does a reverse osmosis system work?
A reverse osmosis system removes sediment and chlorine from water with a prefilter before it forces water through a semipermeable membrane to remove dissolved solids. After water exits the RO membrane, it passes through a postfilter to polish the drinking water before it enters a dedicated faucet. Reverse osmosis systems have various stages depending on their number of prefilters and postfilters.
Waterdrop RO Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration System
Ranked as one of the best reverse osmosis systems, the Waterdrop tankless model has high output for large households. While most RO systems rely on a large tank, which eats up most of the space under your kitchen sink and limits output, this system filters water on demand. The Waterdrop provides an unending supply of treated water, as it doesn’t have to wait for the tank to refill. As a result, it can produce a whopping 400 gallons per day. This system is efficient, producing just 1 gallon of wastewater for each gallon of purified water.
The Waterdrop also includes some excellent features for monitoring the system. A multi-colored LED display provides the status for each of the three filters in its seven stages and the total dissolved solid level of the filtered water in real-time. Keep in mind, however, that this new RO system technology comes with a higher price—up to twice as much as standard RO systems.
Product Specs
- Tank Size: Tankless
- Water Output: 400 gallons per day
- Number of Filtration Stages: 7
Pros
- On-demand water filtration
- Produces 1 gallon of wastewater per gallon of purified water
- Multi-colored LED display
- 3 filters built-in
Cons
- Pricey
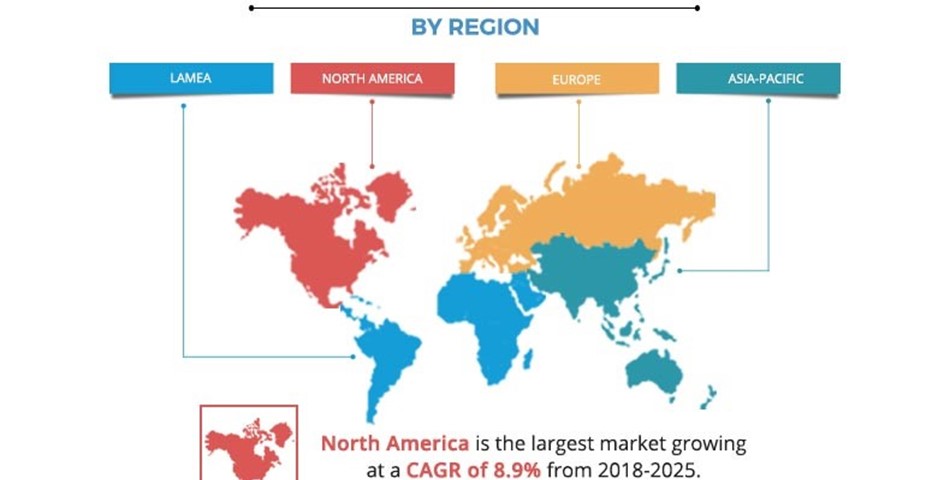
Reverse Osmosis Membrane Market
The global reverse osmosis membrane market size was valued at $6.9 billion in 2017, and is estimated to reach $13.5 billion by 2025, registering a CAGR of 8.7% from 2018 to 2025. n 2017, the spiral-wound reverse osmosis membrane segment accounted for more than two-fifths share of the total reverse osmosis membrane market. There are two main material types of water treatment technology namely, thermal and membrane technology. The membrane technology includes microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis, among others. Reverse osmosis is a form of membrane separation, which uses pressure to force a solution through a membrane that retains the solute and allows the pure solvent to pass to the other side. Typically, this membrane is designed to allow only water to pass through while the solutes (for example, salt ions) are being separated. It is largely used for the desalination of seawater as it can separate dissolved solids, bacteria, viruses, and other selected dissolved substances. The reverse osmosis membrane is essentially non-porous, and it preferentially passes liquid and retains most of the solutes including ions. Reverse osmosis emerged along with electrodialysis as a new technology in the second half of the 20th century and became an alternative to commonly used techniques such as evaporation and distillation.
Considering the rising trend of reverse osmosis membrane use in alternative water source treatment, including desalination plants and wastewater recycling, the reverse osmosis membrane-based water and wastewater treatment processes are expected to have a great potential in the future. Especially in regions with water scarcity, the provision of water from seawater desalination plants is becoming increasingly important. However, the treatment of surface water to potable water will play an increasingly important role during the forecast period.
by Tony Carrick